What is Network Topology?
Network topology can take a while to understand when you are new to this kind of phenomenon. But it is very important to understand the most important elements. This article describes the various technologies of the modern network and various types of topologies.
Network Topology:
Network topology is the arrangement of various objects (links, nodes, etc.) from a computer network. In addition, it describes the architecture, physical format or network structure not only physically but also logically.
There are two types of network topologies:
- Physical Topology
- Logical Topology
Physical Topology:
The physical topology is the visual design of locations, work stations, and cables on the network. Several network elements (or elements) can be configured, including device location and wiring.
Types of Physical Topology:
- Ring topology
- Bus Topology
- Star Topology
- Mesh Topology
- Tree Topology
Ring Topology:
A ring network is a Local Area Network (LAN) where nodes (workstations or other devices) can connect to a closed-loop configuration. Local hosts may connect indirectly, the information passes through one or more locations. This topology applies to a token-based system and the token goes through a loop. Therefore, if the token is free, the node can hold the token and attach the data and the destination address to the token, leaving the token. When a token reaches a destination, the destination ticks data and the token is free to move data.
Additional factors do not affect network performance.
The main weakness of the ring topology is that, if one node fails, the complete network will collapse.
Bus Topology:
Here, at the top of the bus, all nodes (computers, servers, printers, etc.) can connect to one cable. This cable is also known as the Bus that acts as the backbone of the network, connecting each computer and network connection. Both ends of the shared channel have a terminal. Data can only be exported to one location, and once they reach the end, the motive removes the data online.
Therefore, the bus network is useful for smaller networks such as setting up a small office and requires less cable length compared to other topologies. It's easy to connect to a computer and understand. The cost of the bus topology is small.
The disadvantage of the bus topology is that, if any part of the network fails then the whole network closes. It is slower when adding more devices to the network.
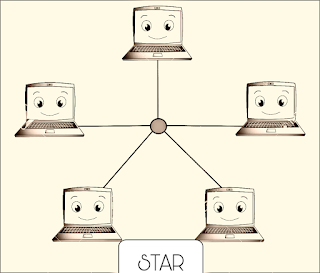
Star Topology:
In Star topology, each node is connected to a central point, called a hub or switch. The central location is the server and the other locations are the client where the data from the source location is first sent to the hub and forwarded to the destination. In star topology, it is easy to insert or delete nodes. Star topology offers better performance because the data does not pass through each location, unlike the bus topology. So, if a particular workstation gets an error then the whole network can be affected. But when the central workspace goes down, the whole network collapses.
Star topology is easy to modify, install, troubleshoot, and new nodes can be easily added without affecting other nodes. Here, the hub can be easily upgraded. The main disadvantage of Star topology is if the entire network relies on a central device. Unfortunately, the central device fails and the entire network stops working.
Mesh Topology:
In Mesh topology, each node is connected to each other and each node sends its signals and transmits data from other locations.
If one of the devices i.e; the node fails, so there is always another offer. In the top mesh, the expansion and modification can be performed without interrupting the other nodes, since the connection is much faster between the two nodes. Disadvantages of mesh topology are expensive because they require long cable lengths and installation and repair are difficult.
Tree Topology:
Tree topology is a combination of tops and Bus and Star another name because it is Star bus topology. Here, the entire network can be split into many parts, which can be easily managed and maintained.
In Tree topology, expansion is possible and easy. While maintenance is also easy.
The disadvantage of a Tree topology is when the spinal cord rupture and the rest of the block shuts down. When the whole network gets bigger it becomes harder to manage and requires more cabling.
Logical Topology:
Logical topology refers to how information can move between two locations on a network. This topology can connect to a network rather than network protocols and explain how data moves across the network.
The network topology is different from one place to another. But, nevertheless, they all have their advantages and disadvantages. If a server problem occurs or the server fails, the topology is responsible for its failure. This is all about network topology and type when you have questions to comment in the comment section below.












0 Comments